Many people consider SSDs too expensive. Yes, it is, but they are really worth their money. Compared with traditional HDD hard drives, SSDs find and transmit the necessary information many times faster, and at their modest size they are able to store a decent amount of data. There are no spindles and other rotating parts, due to which the system loads literally in a fraction of a second, and the computer starts to “fly”. After replacing the magnetic disk with an advanced SSD, you will immediately notice how much faster the PC started to run, opening folders and files at lightning speed. Even the performance of games and applications will increase. True, on one condition: if you competently approach the choice of a hard-core.

Content:
The best SSD manufacturers - which company to choose
Among all manufacturers of solid-state drives, the units boast decent disks. Their devices have really high performance, durable and have an excellent build quality.
When buying a disc of a famous brand, you can not worry about the fact that it will turn out to be faulty, or its passport data will not correspond to reality.
It is to such responsible manufacturers include companies:
- ADATA;
- AMD;
- Intel;
- Plextor;
- Western Digital.
The best solid-state drives of these and several other manufacturers we have already considered in a recent ranking. But whether you need an expensive proprietary device, or you can still do more affordable option? Everything needs to be solved individually.
In addition, there are about a dozen different criteria that must be considered when purchasing an SSD - we will deal with them today.
The principle of operation and the device SSD
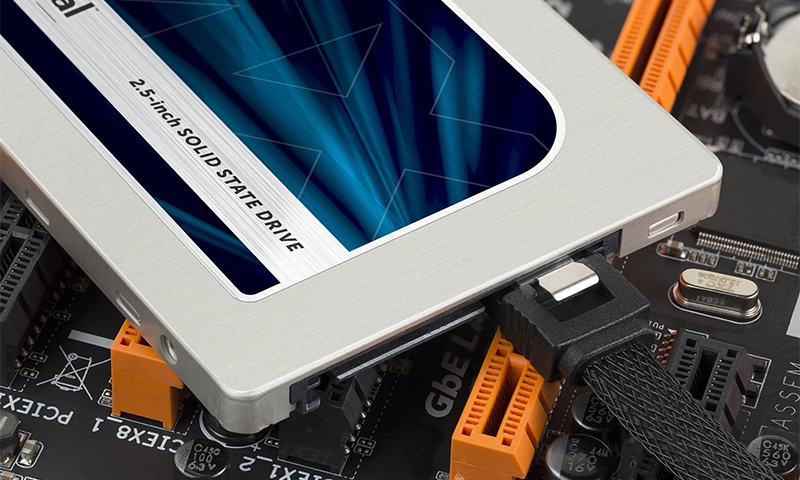

The device of solid-state drives is simple - as all ingenious. In their compact cases there are only a few electronic circuits that do all the work:
1. Blocks of flash-memory - matrix, recruited from the transistor cells, which are written to the data.
2. The DDR DRAM chip is a small chip in which the memory cache is stored. This is the only thing that distinguishes solid-state drives from conventional flash drives.
3. An SSD controller is a chip that is actually a whole block of controllers responsible for reading, writing and placing information in cells.
The principle of operation of the SSD is not particularly complicated. Initially, the device determines the location of the data (searches for the address of the desired memory cell) and immediately starts reading / writing information.
In contrast to magnetic hard drives, you do not need to move the head over the surface of the “pancake” - everything happens at the level of electrical impulses, that is, almost instantly.
The cells themselves are transistors with a gate, which has only 2 positions:
1. "Open" - corresponds to a logical unit;
2. “Closed” - corresponds to zero.
At the time of recording, the gate cells in the array occupy certain positions and can remain in this position for years, preserving the information.
SSD Types
SLC type
This type of disk is considered the most productive (albeit the oldest), therefore it is widely used in server computers. The entry here goes to single-level memory cells, where only 1 bit of information is placed in each - one or zero binary code.
This storage option provides high disk performance and allows you to use the same cell an infinite number of times. The read speed reaches 25 ms.
Pros:
- High speed;
- The possibility of infinite use of the same cell;
- Durability and reliability.
Minuses:
- Cost prohibitively expensive;
- Very modest memory capacity;
- The technology is not new, and it is difficult to find a disk with SLC cells in the free market.
MLC type

In these drives, 2 bits of information are recorded for each transistor. Here, the read speed is no longer as impressive as that of SLC disks (about 50 ms), and the number of rewriting cycles to the same cell is limited to 3000-10000.
Pros:
- Enough high speed;
- Large amount of storage capacity;
- Compact size due to "compacted" data storage;
- More affordable cost;
- Huge selection of drives on the market.
Minuses:
- A limited number of entries on the same cell, with manufacturers constantly reducing it.
TLC type

Here the information is even more compacted: SSD writes 3 bits of data in one cell. Due to this, TLC drives are the smallest in size. But for compactness one has to pay a sharp decrease in the speed of reading (up to 75 ms) and the number of rewriting cycles - up to 1000-3000 times.
Pros:
- High "density" of data storage;
- Compact disk size;
- Low cost.
Minuses:
- A small number of cycles of rewriting information;
- Lowest reading speed.
SSD selection options

Volume
SSD drives still have problems with the amount of information they contain - by this parameter, they noticeably lose to magnetic hard drives. But progress does not stand still, and more and more capacity solid carbide constantly appear on the market.
However, such drives are more often bought exclusively to install the operating system and improve its performance. For games, music, photos and movies in the old fashioned keep HDD.
60 GB of memory is usually allocated for software installation, so a small amount of a solid-state drive will not be a problem. But if you are a professional programmer or just like to experiment with various tasks, buy a 128-256 GB disk - you will definitely have enough of it to work.
Interface type
Currently, SSD drives use interfaces of the following 3 types:
1. SATA 3 - operates at a frequency of 6 GHz, and shows a speed of 600 MB / s.
2. PCI Express 2.0 - has the same operating frequency as the "troika", but it has a higher bandwidth and is 800 MB / s.
3. PCI Express 3.0 - the best interface of all existing today. The data transfer rate is 2-3.2 GB / s.
On the market, you can find some less productive and reliable disk interfaces - these are SATA 1, SATA 2 and USB. But they are suitable only for old-fashioned motherboards, and their characteristics are several times lower than those of the above-mentioned interfaces, therefore it is better to refuse their purchase.
Work speed
It all depends on the budget. The faster the drive, the better for your machine, but the price of SSD increases significantly. In the economy segment, you can count on the read speed of about 450 MB / s and 350 MB / s when writing.
In general, this indicator is influenced by many factors, and the most important of them is the characteristics of the installed controller. Well-known companies do not save a serious approach to assembling a hard disk, and they do not save on the control chip - another reason to buy a brand drive instead of a non-named device with an outdated chip.
Also, when selecting the optimal performance of an SSD, it is necessary to consider the size of its memory. There are more cells in the capacious device, so we need a good speed to read them all quickly.
De-energizing protection
The SSD with DDR3 cache memory needs additional protection against blackouts. This feature allows you to save temporary information on the chips in the event of a power failure of the drive. If you have external protection (for example, a bespereboynik), then the built-in can be neglected.
Availability TRIM
This feature allows you to solve the main problem of SSD - incorrect cleaning of the place occupied by deleted files. Without it, the disk simply "does not understand" that the cells that have become unnecessary can be used for rewriting, and will continue to work with the remaining free space.
As a result, the drive's performance as it fills up will begin to decline steadily, and it will turn into a kind of glass with peas: it seems, there is enough space between them, but it is impossible to stick another “pea” either.
It will take time for the disc to transfer information from the cell to the cache, clear the place, change the outdated data to new ones and only then store them in memory. Naturally, such a multistage process slows down the work of the drive itself and the computer.
TRIM allows you to clean up unnecessary information not at the time of data overwriting, but at any “free” time when the hard drive is least loaded (for example, during idle or background). True, to restore accidentally deleted information is no longer possible.
The TRIM function will be useless if the OS installed on the computer does not know how to work with such commands.
To implement it, we need relatively new operating systems:
1. Windows is not older than 7;
2. Linux starting at 2.6.33;
3. Mac OS X 10.6.6 and higher.
Hidden memory
Each disk has a hidden area of memory that is not accessible to the user. Its cells are used when the arrays of the main workspace fail, which allows to extend the life of the disk.
The hidden area of the SSD can take up to 30% of the total memory of the device, but many manufacturers reduce this figure to 10%, in order to please users by increasing the working space.
Alas, this approach has a serious drawback. When the disk is about 80% full, when transferring data, it starts to “fail”, since its speed drops 2-3 times. In addition, it is on the "spare" cells is located TRIM, which also affects the speed and response time of the computer commands.
Form factor
Under the form factor SSD understand the physical size of the disk, the location of the interface connectors and mounts. But the choice depends on where the hard will be installed:
1. For laptops use 2.5 inch drives.
2. 3.5 ″ disks are installed in the PC system blocks, although if they have special mounts, 2.5 ″ will do.
3. In compact mobile devices work hard drives with a form factor of 1.8 ″ or less.
Body material
Solid state drives can be made of the following materials:
1. Plastic;
2. Aluminum.
It is believed that the second option is better in terms of heat dissipation, but this only matters for very large SSDs.
The fact is that ordinary solid-disks in a computer practically do not heat up. So for the average user it doesn’t matter at all - the plastic case of the drive or aluminum. So, it makes no sense to overpay.
What SSD drive to choose
1. If you want to build a very powerful gaming computer, you need an SSD disk with SLC memory cells. The volume depends on the availability of additional hard HDD: if it is, there is enough hard drive for 256 GB, otherwise it is better to take a model for 500 gigs. The ideal interface is PCI Express 3.0. The form factor will depend on the installation site.
2. Looking for a good, but not expensive SSD? Take a model with MLC cells and a volume within 128-256 GB. Interface PCI Express 2.0 will provide sufficient speed.
3. Need absolutely budget? Then fit a solid-state drive type TLC up to 128 GB with SATA 3 interface. Select the form factor according to the type of computer: 3.5 ″ for the stationary and 2.5 ″ for the laptop.
How much is SSD

1. Drives with SLC memory cells are the most expensive. Their cost starts from 20-40 thousand and reaches 1.2 million rubles.
2. SSD with MLC cells can be purchased from 2000-5000 rubles, if it is a 30-gig device, up to 280 thousand for a 2 TB disk.
3. Low-cost SSD TLC are in the range of 2000-88000 rubles.
It will be interesting to friends too










