Choosing a hard drive for beginners seems like a serious problem. Hard - really complicated and expensive equipment, which determines the work of the entire computer. But even if you do not consider yourself a cool IT specialist, you can pick a good hard drive to replace a failed hard drive or just to expand its capabilities. It is enough to use our advice.

Content:
The best hard drive manufacturers - which company to choose
Even the most eminent manufacturers in the lines of hard drives, which can hardly be called good. So while choosing, although you need to pay attention to the name on the box, you should not dwell on it especially.
Moreover, due to the tough competition of the last decades, the number of firms producing hard drives has seriously decreased. Some simply ceased to exist, others were absorbed by large corporations. As a result, the buyer was left with a poor choice.
The only companies that produce decent hardy and remain afloat today are:
- Seagates;
- WesternDigital;
- Hitachi;
- Toshiba.
Pros and cons of the best models of hard drives from these manufacturers you can see in our ranking. However, you need to choose a hard drive for your computer’s tasks and capabilities, so the recommendations of our experts will be useful to you.
The principle of operation and device hard disk
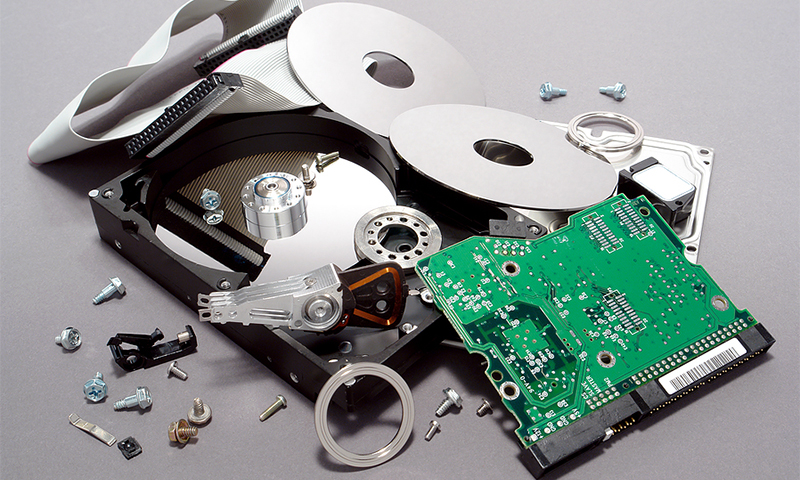

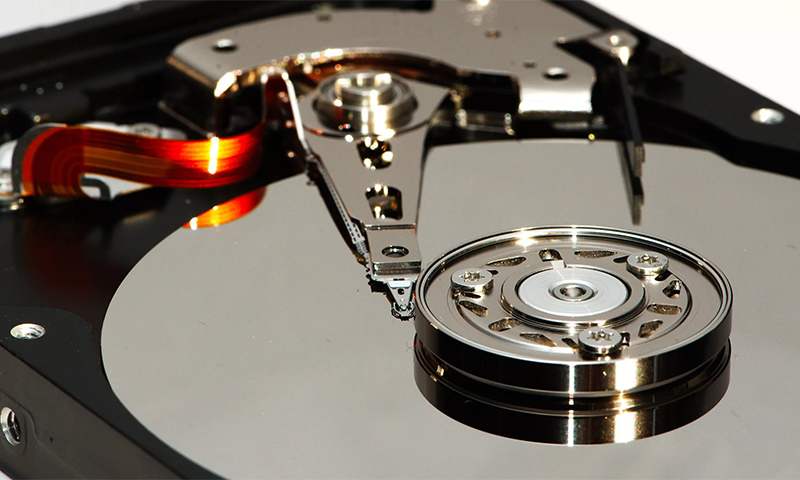
A hard disk consists of two main components: an electronics unit and a pressure zone. To understand how this works, consider each of them separately.
The electronics unit (or control board) is the “brain” of your hard drive. A real computer in a computer with its own processor, which processes the data received from the PC and from the disk itself.
Other important hard drive controls are also located here:
1. Chip cache;
2. The driver that controls the operation of the spindle engine, which turns the wheels;
3. ROM with a set of basic programs to run (may be absent if the functions of this chip are delegated to the processor).
The airbag is a set of high-precision mechanisms enclosed in a casing of durable metal-plastic composite. Most of it takes a package of metal, glass or ceramic disks with a magnetic coating.
It is on their surface that all information is recorded / read. The discs are strung on the spindle of an engine installed here, ensuring their rotation at a speed from 5,400 to 15,000 rpm.
Reading and recording of information occurs due to the block of magnetic heads. The modes of their operation switches the switch-preamplifier, and the movement with respect to the surface of the disks provides a servo with a permanent magnet. In solid state SSD models, all the mechanics are replaced by chips on the platform.
The principle of operation of a classic hard disk resembles a tape recorder: the disc rotates, and the read / write head creates a magnetic field that acts on its surface.
Types of hard drives
IDE interface - minimum speed and volume

Hard IDE-disks assume a parallel connection of drives (hard, CD / DVD-ROM), for which 40- or 80-wire cables with a length of up to 46 cm are used. The throughput of screws with this interface reaches 133 MB / s, and the maximum amount does not exceed 137 GB.
IDE hards are suitable only for old-style computers (late 90s - early 2000s) and are considered obsolete by themselves, but are still on sale.
Pros:
- Low cost - both the hard drive and cables to it;
- To connect the loop does not require terminators;
- Good data transfer rate;
- Easy to configure.
Minuses:
- A small number of connected devices - up to 4;
- Does not withstand heavy loads.
SATA interface - slow but roomy

SATA is a serial interface for exchanging data from drives, a kind of improved version of IDE. The cable size here reaches 1 m, and the volume of the hard itself is 1-2 TB.
Other hard disk drive characteristics depend on the SATA version:
1. SATA 1 - the screw operates at a frequency of 1.5 gigahertz, and its capacity reaches 150 MB / s;
2. SATA 2 - the frequency and throughput of the hard drive doubles, reaching 3 GHz and 300 MB / s.
3. SATA 3 - here the characteristics are doubled again: the frequency is up to 6 GHz, and the bandwidth is up to 600 MB / s.
In general, SATA-drives are not considered the fastest, but very, very capacious.
Pros:
- Reasonably good performance frequency, performance and bandwidth;
- Large amounts of memory;
- Easy to connect - without tedious settings;
- Identical plugs on SATA interfaces of different versions;
- Reliability and long service life.
Minuses:
- High price;
- Short connection cables;
- Not the highest speed.
SCSI interface - high speed, large volume

The most voluminous and fastest hard drives have a SCSI interface and are therefore used in various stations and servers. They have more bandwidth (up to 160 MB / s), but, more importantly, such hard drives can support from 7 to 15 connected devices at the same time.
The length of cables in SCSI hard drives reaches 12 m, and they themselves are very difficult to install. But the volume of their memory allows you to hold about 3 TB of information.
Pros:
- High performance and throughput;
- A large number of simultaneously supported devices - both internal and external;
- Huge amounts of memory;
- The most expensive devices with FC-AL technology allow for “hot” connection.
Minuses:
- Not the most affordable price;
- Difficult to install.
SAS interface - great speed, but small volume

Such hard drives have a universal connector and are perfectly compatible with SATA, if you need to increase the capacity of the drive - its SAS capacity, alas, is often not enough. But such a disk is capable of supporting more than 16,000 devices simultaneously, providing transcendent data transfer rates of up to 6 GB / s due to rotation at high speeds (from 7200 per minute).
Pros:
- Very high performance and throughput;
- Easy installation;
- Compatible with hard drives that have a different type of interface;
- Durability;
- There is a self-diagnosis function.
Minuses:
- Extreme cost;
- Relatively small amount of memory.
SSD
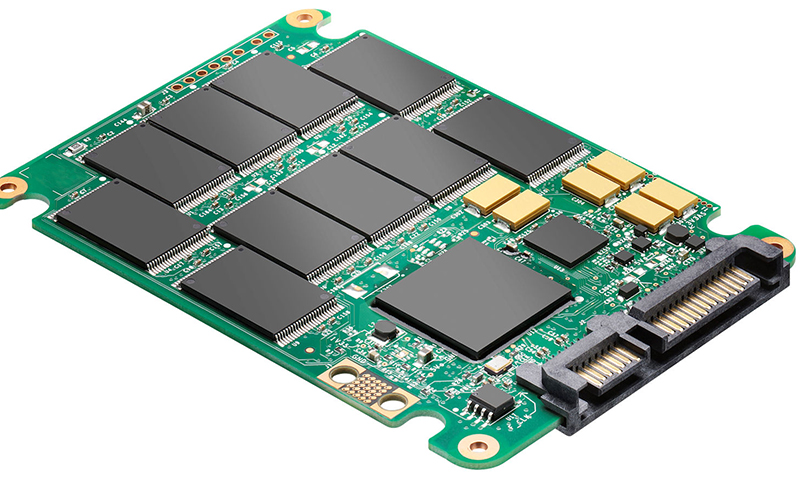
Back in 2009, there was nothing to replace the usual HDD hard drive. Today, its functions may well take over or complement more productive SSD - Solid-State disks. There are no moving parts in these solid-state drives, and they themselves are a set of flash-memory chips located on the same board — in other words, they are very large flash drives.
Pros:
- Unrealistically high speed;
- "Vitality" - there is no delicate precision mechanics that requires careful handling;
- Compact size and low weight;
- Low energy consumption;
- Absolutely silent operation;
- The ability to combine SSD and HDD.
Minuses:
- Very high price;
- There are restrictions on rewriting cycles - as soon as the limit is reached, the disc will require replacement.
Hard disk selection options
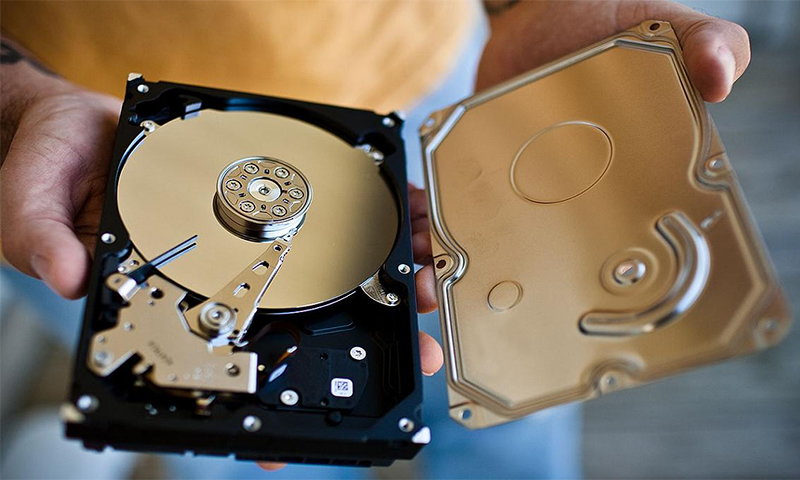

Memory
This is a very important indicator when buying, and here you need to follow the principle: the more, the better - sooner or later you fill your screw to the limit. But a larger disk and more expensive, so try to pre-establish for themselves reasonable boundaries.
Decide what you need a computer for:
1. For work with documents and office programs, 500 GB hard drive is enough for the eyes;
2. For games and multimedia, choose a hard drive from a terabyte and above.
The main thing when buying a powerful hard drive is to remember that not every computer will pull it. To eliminate the error, look first in the “Boot” settings, what kind of firmware do you have: BIOS or its more modern version - UEFI. In the first case, there is no point in cramming a hard disk of more than 2 terabytes into the computer, but in the second case, you can assume that your hands are untied.
Work speed
A large disk does not guarantee fast machine operation. Although the size still indirectly affects the speed, since on a voluminous hard drive the recording is “denser”, which means that a little less time is spent on data processing.
Nevertheless, pay attention to the hard disk performance specified in MB / sec and look for the highest possible value in your price category. Now in stores you can buy screws that work at speeds from 150 to 600 MB / s, and if you fork out the SAS interface, then up to 6 GB / s.
Spindle speed
This indicator determines the number of revolutions of the magnetic disks on the axis per unit of time (usually per minute) and affects the performance of not only the hard drive, but also the computer. The faster the spindle rotates, the better and quieter your hard will be.
In most cases, the spindle rotates at a speed from 5,400 to 7,200 rpm. But there are models that easily develop 10-15 thousand rev / min. Yes, they are “more responsive” in their work, but they are also expensive.
Clipboard size
The hard drive uses the internal memory (cache) most often. In most cases, hard drives have a multiple of 8 cache size: from 16 to 64 MB. You don’t feel much of a difference between them, but for better and faster hard work you should choose a larger buffer - 32 or 64 MB.
Form factor
In fact, this is just the size of the hard drive box, but it’s exactly what determines where your screw will fit, and where it just won’t fit.
Here, manufacturers offer to build on the thickness in inches:
1. 1.8 ″ - with their small capacity, these mini-winchesters are quite expensive and therefore not received much spread.
2. 2.5 ″ - are mainly used in laptops, because they are lightweight and consume relatively little electricity (2-2.5 W). Sometimes these hard drives are installed in home multimedia systems.
3. 3.5 ″ are “big” disks with good memory capacity (today there are models that reach 10 TB), but they are suitable only for installation in a PC system unit and for work they require 7-10 W of energy.
Memory chips (for SSD)
If you decide to fork out on a solid-state drive, you should consider the existing limitations of overwriting.
It all depends on the technology used in memory chips:
1. SLC - cells in such a chip contain only 1 bit of information (in binary code 1 or 0). But they are distinguished by high speed of work and are able to withstand up to 100 thousand recording cycles.
2. MLC - store 2 bits on each cell, because of what the size of these hard drives will be half the size with the same amount of memory. They work slower than SLC and have a limit of 10 thousand cycles, but they are much cheaper.
3. FRAM is a relatively new technology that has not yet gone to the masses. There is also a finite value of rewriting cycles, but the limitations are so conditional that they are not worthy of attention. Such a solid-state drive should work for about 40 years without stopping in order to exhaust its resource.
Which hard drive to choose

1. If you need the cheapest hard drive (for example, to perform simple tasks on a PC), choose an HDD that has up to 500 GB of memory and 16 MB of cache.
2. The SATA interface is suitable for computers younger than 10 years old, the "old men" will most likely need an IDE.
3. Preference is better to give the form factor of 3.5 ″, but if there are connectors for 2.5 ″ - choose any of these options.
4. A performance of 150 MB / s and a rotation speed of 5400 rpm will be sufficient. Of course, such a hard noisy, but it will be almost one and a half times cheaper than faster screws.
5. If you want to build a powerful gaming computer, it is better to immediately purchase 2 types of disks - HDD and SSD.The first one should have a memory capacity of at least 1 TB - you will use it to store personal information (photos, videos, documents, music, etc.), and on the second, “hang” the operating system, powerful games and resource-intensive programs.
6. Do you want a powerful computer, but you don’t have enough money to buy two hard drives together? Choose one - the one that can afford, but try to get closer to the "game" indicators. The only thing - for hard, you can reduce the cache requirements to 32 MB.
How much is a hard disk
HDD:
1. Models with IDE interface cost from 2,000 to 50,000 rubles;
2. SATA 1-3 starts with 3300 rubles. and comes to 1.5 million;
3. SAS is even more expensive - from 5,000 thousand to 7 million rubles;
4. The SCSI interface will please a relatively affordable price in the range of 4-620 thousand.
SSD:
1. The cost of SSD with MLS-cells ranges from 4,000 to 2 million rubles.
2. Prices for SLC long-livers are much higher - from 40 thousand to 12 million rubles.
It will be interesting to friends too







