RAM is one of the important components of a computer that directly affects its speed. That is why many seek to maximize the OP, adding strips or changing the old to more "roomy" modules. However, the features of the motherboard and processor installed in the PC, impose serious restrictions on the choice of a particular type of RAM. And without knowing all the nuances, you risk buying an inappropriate bar or overpaying extra money for a device that cannot reach its full potential.

Content:
The best manufacturers of memory rails - which company to choose
A variety of slats OP confuses even experienced professionals, not to mention the beginners. After all, dozens of famous and little-known companies are engaged in their production.
You need to focus on the products of brands with a good reputation - they usually do not have a marriage, and all schemes work stably. Yes, you have to overpay for a big name, but it's worth it.
Good RAMs are produced by the company:
- Crucial;
- Corsair;
- HyperX;
- Goodram;
- AMD
The best memory modules for computers and laptops We recently reviewed in one of the reviews. All of them are good in their own way, but when choosing a specific plank for your car you need to take into account a number of important parameters. We will talk about them today.
The principle of operation and the device memory
The operating system looks simple: it is an electronic board with chips soldered to it. They are the memory chips that collectively create the core (or matrix) for recording information. Contacts are located in the lower part of the board, and between them there is a key - a recess under the return tab on the motherboard connector.
To read information from a specific memory cell of RAM, the processor sends an electronic signal to the line in which it is located. After an identical "request" is sent to the column of the matrix.
This allows the computer to quickly find the necessary data and continue its work without delay. Information in the cells of the OP is stored while they are powered. Once the device is disconnected, all data is instantly lost.
Types of RAM
DDR
Development of the far 2001, which at that time just blew up the computer world. Its volume rarely exceeds 512 MB, and it works with a frequency of only 400 MHz. For connection to the board, 184 contacts are brought out to the edge, power is provided with a voltage of 2.2-2.4 V.
All these figures indicate that this subspecies of the OP is outdated, and for a long time. The first DDR is suitable only for computers of the 2000s, whose owners do not want to change the filling completely. It is difficult to find it in the free market, so in search of such a bar you will have to go around more than one flea market.
Pros:
- Able to improve the speed of the old computer without a complete replacement of the filling;
- Low cost.
Minuses:
- Poor performance;
- Small amount of memory;
- Hard to find in the free market.
DDR2
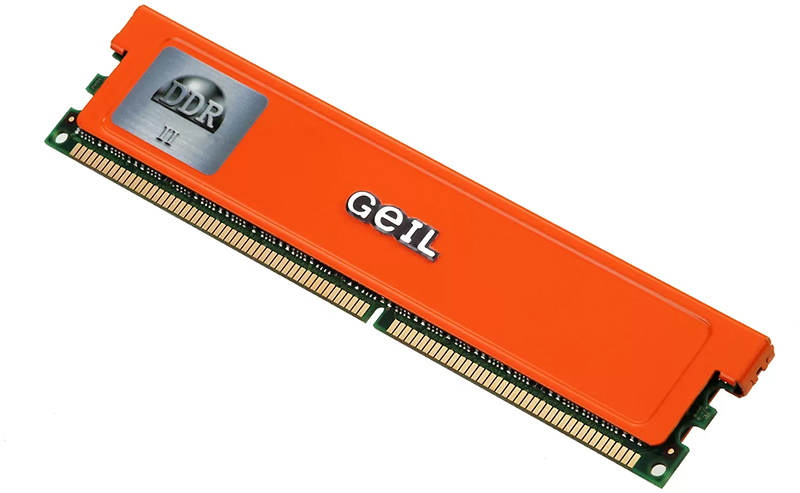

This is a more advanced model developed in 2003. The number of contacts compared to the previous version here has increased to 240, which made it possible to significantly speed up the transfer of data to the processor. The clock frequency has also increased - 2-2.5 times (800-1000 MHz).
At the same time, the power consumption of the module decreased to 1.8-2.1 V. All these improvements allowed DDR2 to successfully replace its predecessor. But her time is also running out, although in many middle-aged machines such slats still work.
Pros:
- In all respects, it is almost twice as large as the pilot models;
- Allows in the old device does not change the expensive components, but simply add another OP bar.
Minuses:
- Weak performance by current standards;
- Unreasonably high price.
DDR3
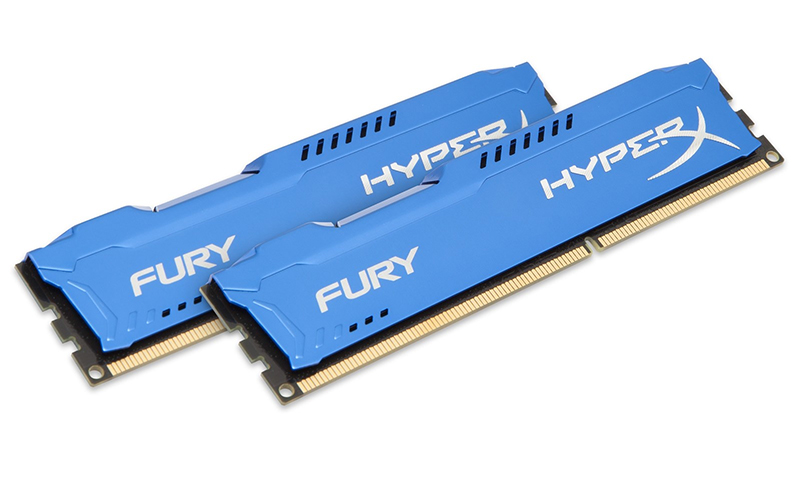

These modules were created in 2007 and have been very popular for a decade. But the most pleasant thing is that they will not soon disappear from the stores.
Compared to the previous version, the number of contacts has not changed here, but the form factor has changed, which does not allow DDR2 to be changed to a troika just like that. The clock frequency of the modules in the third generation has almost tripled, reaching 2800 MHz, however, the timings (delays) have become higher.
Manufacturers also continued to work on reducing energy consumption and were able to achieve impressive figures of 1.5 V and 1.35 for DDR3L strips. In general, we can say that the “troika” has become 30% more efficient than its predecessors.
Pros:
- Compatibility with almost any current motherboard and processors (with the exception of frankly ancient models);
- Fast enough data processing;
- Easy to find on sale.
Minuses:
- Only suitable for expansion - there is no point in buying a new DDR3 car.
DDR4
Designed in 2012 with a huge bandwidth (25.6 GB / s) and a frequency that grew to 4,100 MHz. Despite such high performance, power consumption of fourth-generation RAM is quite small — only 1.05 V.
Alas, the changed form factor does not allow using it to improve the performance of computers with old types of DDR connectors.
Pros:
- Maximum performance for today;
- Huge bandwidth;
- Low power consumption;
- Cost at the level of DDR3.
Minuses:
- Incompatibility with previous versions of OP.
RAM selection options
Purpose
The levels of the OP for computers and laptops do not differ in characteristics, but have a different panel size. Modules designed for PCs are simply DIMM-signed, while for laptops SoDIMM is used.
Owners of laptops will also have to carefully consider the choice of RAM, since inside compact machines there are few slots for slats - 1, maximum 2.
Volume
This is the main criterion for which you need to focus when buying an OP. Many believe that the more this indicator - the better. Of course, they are right, but this is not a reason to tamp additional modules into all the free slots of the system unit.
The computer's processor, like the operating system, can use only a certain number of gigabytes — the machine simply does not see the remaining devices, and you will spend money in vain.
For example, 32-bit Windows configurations are designed for only 3 GB, but 64-bit and 2 will be small - it is more comfortable for an OS to work with 4-gigabytes bars. New versions of “windows” (starting with Win 8.1) will require 8 GB at all - in this case you will get the best system performance.
Nevertheless, there is no need to be greedy either - if your machine does not have enough RAM, it will start borrowing megabytes of memory from the hard drive, and taking into account the principle of its operation, this will not do it good. Due to the constant movement of heads, which takes time, the computer will freeze.
Select the volume of the OP according to your objectives:
1. Less than 2 GB is enough for working (office) computers or old-style PCs.
2. 2-4 GB - enough for "easy" games, access to the Internet, watching movies and other not too resource-intensive tasks.
3. 4-8 GB - the best option in terms of price / volume. This RAM will cope with the work of previous versions much faster and will be able to pull even serious video games, at least at the minimum settings.
4. 8-16 GB - an excellent indicator for gaming computers of medium and high class.
5. Over 16 GB - suitable for solving any problems up to professional and will not require updating the computer for the next few years. But ordinary users just do not need so much RAM.
Frequency
It depends on the speed of the RAM - the higher the clock frequency, the faster your computer will be.However, you should not chase after the ultra-high characteristics of the OP module, if the processor and the motherboard do not support them - you simply overpay for something you cannot use.
Budget computers and laptops usually do not support DDR4 RAM over 2400 MHz, although powerful machines are already quite capable of the frequency at the level of 3800 MHz. But this applies exclusively to new technology. But in previous generations of PCs working with DDR3, the restrictions are much tougher - many of them are capable of “making friends” only with modules issuing from 1333 to 1866 MHz.
Timings
This is an indicator of the delay between operations in the depths of memory. The less they are, the better, because each stop is reflected in the speed of the computer. Here we have to look for a compromise, since there is another pattern: with an increase in the clock frequency of the OP, the timings also increase.
Reasonable delays in the range of 9-11 units are characteristic of a low DDR3 frequency, while in DDR4 this figure can reach 15-16.
Voltage required
You need to pay attention to this criterion only if you acquire the bar for upgrading the car. The motherboard distributes the same voltage to all connectors of the OD, even if they are designed for different types of memory. When choosing, simply focus on the load of the old module, then the new one in its place will work without problems.
Distortion voltage in one direction or another can seriously harm the other components of RAM. If you do not have enough power, you will get a destabilized system, and applying too high a voltage (if the motherboard “decides” to orient to a more powerful module) will disable the remaining strips.
The presence of radiators
Ribbed linings on the OP modules are needed not for beauty, but for the discharge of excess heat. You can't do without them if you take hot DDR3 with a high clock frequency (more than 1866 MHz) or DDR4 from 3000 MHz. In other cases, it is just an expensive and useless decor that collects dust on itself.
What RAM to choose
1. If you need RAM to upgrade a very old computer, you will have to run around looking for DDR strips or fork over DDR2 - it all depends on what type is supported by the existing motherboard and processor.
2. Those who update the work computer, you can take DDR3 with a capacity of about 2-4 GB with a frequency of up to 2500 MHz.
3. To build a new car (regardless of its purpose), you need to buy only DDR4, with a capacity from 4 to 8 GB with a good clock frequency. But it’s not worth going beyond 3000 MHz, since many processors stop working steadily when this threshold is exceeded.
4. Gamers should also turn to fourth-generation high-frequency strips of 8–16 GB and above. Only it is better to take a couple of modules at once to get twice the amount of memory.
Cost of RAM
1. The old DDR bar can be found at prices ranging from 400 rubles (256 MB) to 50,000 (4 GB).
2. DDR2 for 512 MB will cost at least 350 rubles, and for a capacious 8-gig model you will have to pay from 8 to 27 thousand.
3. DDR3 RAM costs between 450–90000 rubles (1–32 GB, respectively). Low-models with a capacity from 2 to 32 GB are on average cheaper - from 800 to 36 thousand rubles.
4. For the DDR4 bar with a volume of 4-64 gig will have to pay from 2 to 87 thousand.
It will be interesting to friends too