Problems with the endocrine system, overweight, a rigid diet, old age - all these are the "indications for use" of the meter. This device is intended not only for diabetics (although they have to measure blood sugar levels more often than others) - many healthy people will not be hurt by such a home mini-laboratory. But having no experience in handling such equipment, it is difficult to make the right choice. Let's consider together the main types of blood glucose meters, their principle of operation - and then we will decide which device should be in the first-aid kit.

Content:
The best manufacturers of blood glucose meters - which company to choose
All manufacturers of medical devices in one voice promise us measurement accuracy and comfortable use. But do not blindly believe advertising. There are enough well-established companies on the market, whose products are really trustworthy and receive positive feedback from both physicians and their patients.
The most accurate glucometers produce well-known brands:
- Bayer Health Care;
- Life Scan;
- Roche;
- Omelon;
- Elta
In their assortment you can find excellent models with different speed test results and the number of blood sampling - the best of them fell into our rating.
If you do not have time to understand all the nuances, you can safely buy any of the devices presented in the review. Well, for those who like to make informed decisions, we suggest to get acquainted with all the possibilities of modern blood glucose meters.
The principle of operation and the device meter

Most blood glucose meters work on the same principle. You need to make a puncture in the pad of your finger and apply protruding blood to the test strip. Its surface is treated with a special reagent, which upon contact with glucose changes its properties.
A strip of blood is inserted into a special socket of the device, and then everything will depend on the type of device:
1. Photometric will determine the change in color of the reagent;
2. An electrochemical blood glucose meter will measure current using its electrodes.
Despite the apparent complexity of the analysis, the meter itself is a fairly simple, albeit a smart device. Its main elements are:
1. Compact housing;
2. The display, which displays all the information about the composition of the blood and the device;
3. Scarifier or lancet for skin puncture;
4. Nest where test strips are inserted;
5. The analyzer itself is electrode or optical.
Technologies do not stand still, and today glucometers, which do not require any punctures, have increasingly begun to appear. Manufacturers while experimenting with non-invasive devices, using ultrasound, electromagnetic pulses and spectral analyzers. Behind such devices is the future, but for the most part they are not yet available, and many developments are still damp.
Types of blood glucose meters
Photometric
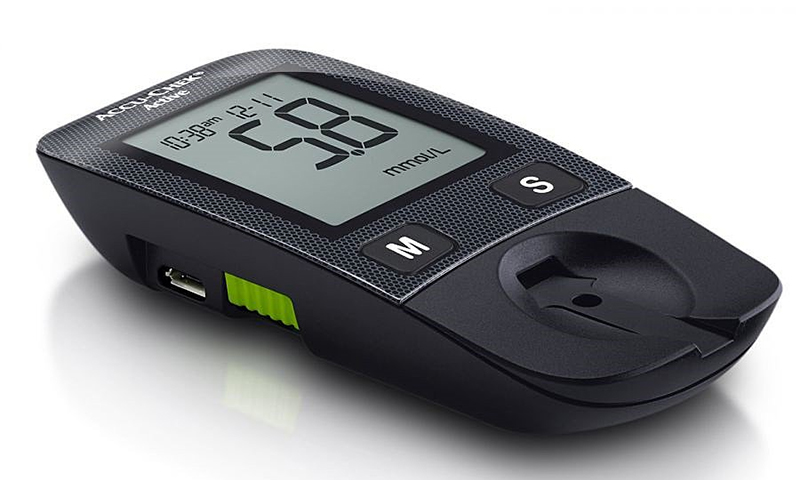

Glucometers “veterans” were the very first mini-laboratories for diabetics. And although they are already being squeezed out by more advanced models, some still prefer to use these old people. They are not worse than our eyes; they recognize the change in shade of the test strip and compare it with the standard color scale, deciphering the result and translating it into a numerical format.
Of course, a person himself could compare the color of the reagent with a tablet, but the trouble is that in diabetics the development of the disease often leads to vision problems and at least worsens color perception.
Pros:
- Convenient and easy to use;
- Data can be transferred to a computer;
- Measurements are stored in the device memory, which will calculate the average for a certain period of time;
- It is completed with own needles, a lancet, test strips.
Minuses:
- Not in great demand and gradually disappear from sale;
- Fragile, require special care;
- The hue of the reagent can change not only under the influence of carbohydrates, but also when the temperature changes, which gives a certain error.
Electrochemical

Today it is the most common and accurate blood glucose meters, which determine the composition of blood by measuring electrical current. It occurs when the glucose reaction with the test strip is coated - the higher the blood sugar level, the greater the charge force will be in the reacted segment. The device will only measure it and display data on the display.
The figures obtained in this way are more accurate than in the photometric apparatus. In addition, modern electrochemical glucometers are not limited to glucose, but additionally check the level of cholesterol, ketones and triglycerides in the blood.
Pros:
- Functionality;
- High measurement accuracy;
- For analysis, you need very little blood;
- The availability of test strips;
- The result can be obtained in 5-10 seconds;
- Long service life;
- Large selection of various models - for children, visually impaired, the elderly, etc.
Minuses:
- Almost all models come with encoding, which causes difficulties for older people;
- The reacted test strips have a short period of activity, so you need to do everything quickly.
Non-invasive (optical)
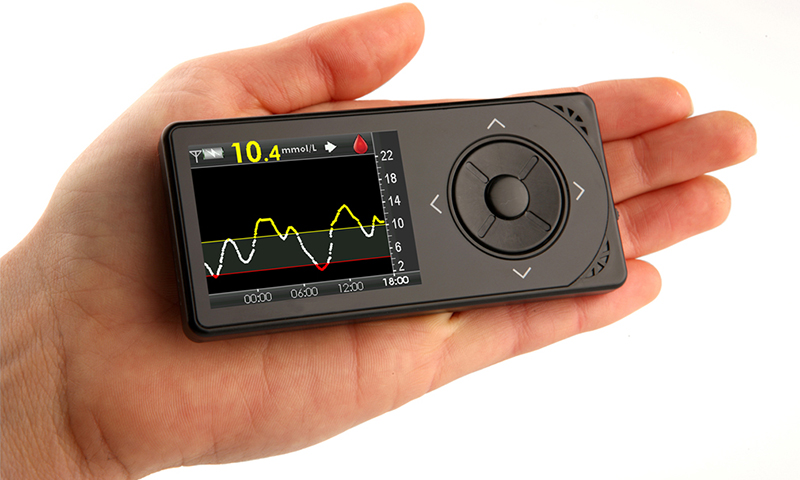
Such blood glucose meters are few, but amazing variety. Some determine the level of sugar by analyzing muscle tone, others based on pressure measurements, others use ultrasonic, thermal and electromagnetic waves. But everyone has one thing in common - they don’t need blood for testing.
Non-invasive devices are still under development and improvement both in Russia and abroad, but some models are already on sale.
Pros:
- Do not require a puncture of the skin and the use of test strips;
- Acceptable measurement accuracy;
- Automatically shut off after the study;
- At the same time, blood glucose and blood pressure are monitored.
Minuses:
- Overall;
- Expensive and pokka not particularly affordable.
Meter selection options

Result calibration
So called the method of blood tests, which uses a blood glucose meter in their work.
There are two options here:
1. For plasma (venous blood) - this is how they determine the presence of sugar in clinical laboratories, obtaining the most accurate results of the analysis. With this calibration, most modern blood glucose meters work.
2. For whole (capillary) blood - always gives an underestimate result - by about 11-12%. That is, to get accurate data, the figures from the display need to be corrected by multiplying by a correction factor of 1.11. However, now many glucometers calibrated for whole blood automatically recalculate the results of the analysis.
Both methods are suitable for control. The only question is what indicators you and your doctor are used to using.
Volume of blood sampling
The description of each model indicates how many microliters of blood is needed for one test. It is believed that the smaller this figure, the better - no need to make too deep a puncture.
In fact, everything is individual here.
1. Children and adults with diabetes of the first type should not drive the scarifier deeply - they need an apparatus that takes from 0.5 to 1-1.4 μl.
2. In older people, blood circulation is often impaired, and in order to make a puncture of the desired depth, you have to take a blood glucose meter for 2-3 μl.
When buying, do not forget to clarify whether it is necessary to drip blood onto a test strip or after the injection the device itself draws the necessary amount into the analyzer.
Result accuracy and coding
No matter how perfect the home apparatus is, it will never replace laboratory tests, but only give approximate figures. The percentage of discrepancies can vary between 5–20%, but even such an error is not critical and is considered normal.
Even the type of test strip can affect the measurement accuracy. To avoid this, they began to use a coding system in glucometers, which allows them to “synchronize” the device with testers of different sensitivity.
As a result, it was possible to achieve more correct numbers, but work with coded devices became much more complicated. For example, it is difficult for older people to master technological innovations - it is better for them to purchase blood glucose meters and strips without coding.
Computation speed
The parameter is doubtful, since all modern analyzers work pretty quickly. The most nimble models give accurate data after 5 seconds, the most “slow” - after 10. The difference of 5 seconds is rarely crucial, but many people like fast devices.
In fairness, we note that there are still devices on the market that calculate the results for about a minute. These are suitable only for periodic testing of the blood in healthy people and patients with diabetes of the second type.
Memory
But this factor is very important, because the memory of the meter transforms it from a simple “laboratory assistant” into a doctor who tracks the dynamics of the disease. The device can not just record all the measurements, but also compare them with each other, share the indicators before and after meals, and display the average result over a certain period of time.
1. If you do not keep a special diary or do it irregularly, you need a meter with a large amount of memory that can hold about 500-800 measurements.
2. With frequent use of the device, it makes sense to look for a model with 2000 entries.
3. Those who simply monitor their health will have enough of a device that stores 40-50 analyzes.
Modern devices also allow you to transfer all stored data to a computer via the supplied USB cable.
Which meter to choose

1. If you do not have serious health problems, and you just want to buy the device, so to speak, for prevention, you should not spend money on expensive models. Take a domestic photometric blood glucose meter, with a good memory capacity of 250-500 measurements.
2. Patients with type 2 diabetes and complications such as obesity need a complete biochemical instrument that simultaneously measures the level of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood. A large amount of memory is welcome, but is not mandatory, since analyzes will have to be carried out only 2-3 times a month.
3. If you need constant glucose monitoring, that is, people with the first type of diabetes, it is better to purchase an electrochemical device that works with cassette test strips. In this case, you will not have to change them after each check and re-enter the code. By the way, the coding here is vital - it will allow you to accurately determine the required dose of insulin.
4. Older people need to use a blood glucose meter with a large display and large numbers. Not bad, if it will provide a system of sound signals, which will alert you to incorrect measurements or excess glucose. A minimum of buttons, a wide nest for test strips, no coding and blood sampling within 2-3 μl is an ideal device for diabetics of advanced age. The function of the tonometer will also not be superfluous.
5. Lovers of tech gadgets and people who are tired of constant puncturing fingers, you can search for an expensive novelty - a non-invasive blood glucose meter.
How much does a blood glucose meter

1. A photometric device with plasma calibration can be purchased from 700 to 4000 rubles.
2. An electrochemical device with the same type of calibration will cost 600-9500 rubles.
3. Devices that analyze whole blood, costing only 800-1700 rubles, but also not widely represented on the market.
4. A non-invasive glucometer of a new generation from a domestic manufacturer will cost at least 7 thousand rubles.
It will be interesting to friends too